- Build a 5V USB Power Socket with LM317L Circuit
- USB Switch Circuit: Connect Printer to PC or Laptop
- USB Printer Share Switch: Simple Circuit Design
- USB Power Injector: Circuit Diagram for External Drives
- USB-Powered Appliance Circuit: 150W Triac Control
- USB Current Limiter Circuit Design with MAX1562
- USB Brightness: A Tiny Circuit Spark
USB Current Limiter Circuit Design with MAX1562
Description
Modern life would be significantly impacted without essential computer peripherals, such as a USB-powered teacup warmer. While a productivity tool for many users, this device poses a potential risk of localized motherboard meltdown due to excessive current draw from a USB port. Similarly, a poorly wired connector during prototyping and development of a USB-powered peripheral could lead to damage. Protective measures, like current limiting or fuses, are necessary to safeguard electronic components.
MAX1562
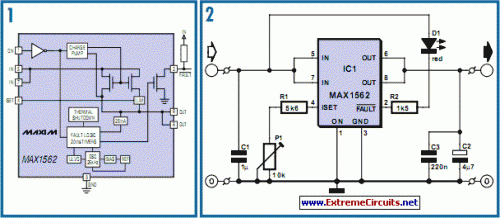
The MAX1562, as depicted in Figure 1, is a specialized USB current limiter produced by Maxim Integrated. It operates effectively with a supply voltage ranging from 4.0 to 5.5 V, exhibiting a typical operating current of 40 µA or 3 µA in standby mode. The circuit incorporates a very low resistance in the power line (usually 26 m, but guaranteed less than 50 m) achieved through an internal MOSFET. The FET gate bias voltage is generated on-chip using a charge pump circuit.
MAX1562
The device accurately differentiates between an overload and a short-circuit condition within the power supply by measuring the voltage drop across its internal resistance. If the voltage falls below 1 V, a short circuit is assumed, triggering a (limited) output current pulse every 20 ms to attempt to restore the output voltage. This mechanism is effective against scenarios like large capacitors across USB supply pins or the in-rush current of an external hard drive during startup. If the supply rail isn’t pulled up within 20 ms, the FAULT output (pin 2) is driven low. The output current limit is determined by a single resistor on pin 4 (ISET): LIM = 17120 / RSET.
MAX1562
The circuit incorporates a fixed 5.6k resistor in series with a 10k preset, offering an adjustable current limit between 1.097 and 3.057 A. This range generally satisfies most application requirements. Reducing the preset resistance lowers the current limit level. Any intermittent connection within the preset (due to a dirty track, for instance) will activate the chip’s shutdown function. The MAX1562 also contains a thermal cut out which disables the output when the chip temperature exceeds 160 degrees C.
Figure 2 illustrates a diagram of the manufacturer’s application circuit. The FAULT output drives an LED through a series limiting resistor, reducing the LED current to 2 to 3 mA. The MAX1562 is available in a HESA variant (with an active high ON signal) or ESA version (with an active low ON signal). The chip is packaged in an 8-pin SMD outline. Figure 3 shows a small PCB layout for the circuit utilizing primarily SMD components.
COMPONENTS LIST
- R1 = 5.6k (SMD 1206)
- R2 = 1.5k (SMD 1206)
- P1 = 10k preset
- C1 = 1µF (SMD 1206)
- C2 = 4µF7 10 V, tantalum
- C3 = 220nF (SMD 1206)
- D1 = LED, low current
- IC1 = MAX1562ESA
circuit from http://www.extremecircuits.net/2010/05/usb-fuse.html