Build Your Analog Telephone Line Monitor Circuit Diagram
Circuit Diagram
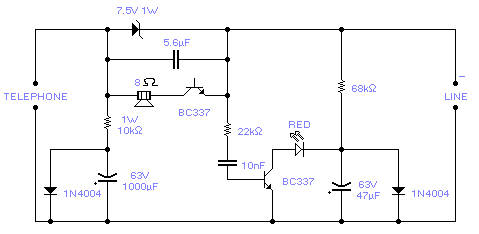
A detection circuit has been developed to identify anomalies within telephone lines. This design identifies the presence of an extraneous telephone connected to the line, detects instances of a short circuit or an open connection. An audible alert, combined with a visual indicator via a flashing LED, provides immediate feedback on the line’s condition. The speaker functionality is disabled during standard conversations, ensuring privacy. Power for the circuit is drawn directly from the telephone line, eliminating the need for an external power source. Transistors are configured in a reverse-biased manner, functioning as oscillators within the system. Consideration could be given to utilizing a 2N2222A as a substitute, though this option has not been experimentally verified. This monitor is, of course, exclusively intended for analog telephone lines. Careful attention must be paid to the input line’s polarity; while a polarity reversal will not damage the circuit, proper operation will not be achieved.
2N2222A Details
The circuit heavily relies on the functionality of the 2N2222A transistor. This is a versatile NPN bipolar junction transistor, commonly employed in switching and amplifying applications. It is a three-terminal device – Base, Collector, and Emitter – designed to control the flow of current between its collector and emitter terminals based on the applied current or voltage at the base. The 2N2222A is known for its relatively high current gain and moderate switching speed, making it suitable for various electronic circuits. It’s crucial to understand the operating characteristics of this transistor – particularly its voltage and current ratings – to ensure proper circuit design and avoid damage.
circuit from http://www.electronics-lab.com/