Stereo to Mono Converter: Build Your Simple Mixing Circuit
Description
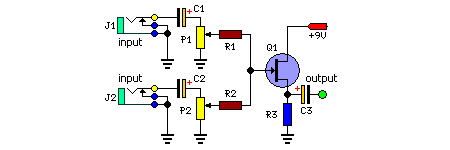
This basic circuit combines two or more signal pathways into a singular pathway (for instance, stereo audio into mono). The design accommodates a varying number of channels, exhibiting minimal power consumption. The mixer is presented with two input points, yet it can accept a multitude of channels simply by replicating the “input sections,” as highlighted in the schematic diagram.
Circuit Diagram:
Parts:
- P1 = 10K-50K Potentiometer
- P2 = 10K-50K Potentiometer
- R1 = 100K
- R2 = 100K
- R3 = 6.8K
- C1 = 0.1uF-25V
- C2 = 0.1uF-25V
- C3 = 0.1uF-25V
- Q1 = 2N3819 Junction Field-Effect Transistor
- J1 = Audio input connectors
- J2 = Audio input connectors
Notes:
- A number of channels, as needed, can be incorporated into the mixer.
- This can be achieved by duplicating the "input sections," as clearly demonstrated in the schematic.
- An instance of this mixer was observed with eighteen input points.
- A shielded enclosure is likely required to mitigate hum and prevent oscillations.
- P1 and P2 function as dual-gang potentiometers for a stereo configuration.
- The circuit is capable of being powered by a single 9 volt battery.
More about components
Junction Field-Effect Transistors (JFETs), such as the 2N3819, are semiconductor devices that operate as voltage-controlled resistors. They are commonly employed as current sources, switches, and in amplifier circuits. The 2N3819, a popular N-channel JFET, utilizes the gate-source junction to control the flow of current between the drain and source terminals. The transistor's characteristics allow for precise current regulation and amplification, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications. Its small size and relatively low cost further contribute to its widespread adoption in circuit designs. The device exhibits a moderate drain-source on-resistance, typically ranging from 100 to 300 ohms, depending on the operating conditions. This on-resistance is crucial in applications where current control is paramount.