Build Your DIY Soldering Iron Inverter Circuit (230V)
Description
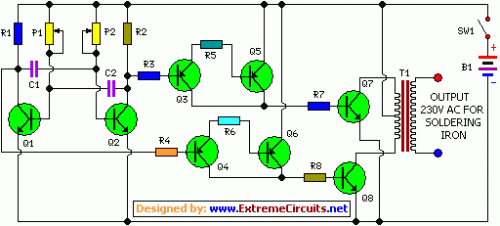
Here is a straightforward and economical inverter designed for operating a small soldering iron (25W, 35W, etc.) in the absence of a standard power supply. It incorporates eight transistors and a few resistors and capacitors. Transistors Q1 and Q2 (each BC547) establish an astable multivibrator that generates a 50Hz signal. The complementary outputs from the collectors of transistors Q1 and Q2 are supplied to npn Darlington driver stages constructed by transistor pairs Q3-Q5 and Q4-Q6 (utilising BC558 and BD140).
The outputs from these drivers are then fed to transistors Q7 and Q8 (each 2N3055) arranged for a push-pull configuration. Appropriate heat sinks should be applied to transistors Q5 through Q8. A 230V AC primary to 12V-0-12V, 4.5A secondary transformer (T1) is utilized. The center-tapped terminal of the secondary of the transformer is connected to the battery (12V, 7Ah), while the other two terminals of the secondary are connected to the collectors of power transistors T7 and T8, respectively.
When power is applied to the circuit via switch S1, transformer X1 produces 230V AC at its primary. This voltage can be utilized to heat a soldering iron. The circuit should be assembled on a general-purpose printed circuit board and housed within a suitable enclosure. Connect the battery and transformer using appropriately sized current-carrying wires. Position a power switch S1 and a 3-pin socket for the soldering iron on the front panel of the box.
Integrated Circuits – Details
The BC547 transistor is a versatile NPN bipolar junction transistor widely employed in various electronic circuits due to its general-purpose characteristics and robust performance. It's commonly found in switching and amplification applications. The BC558 is a general-purpose NPN transistor, known for its reliability and moderate gain, frequently used in switching and small signal amplification circuits. The BD140 is a power transistor, specifically designed for higher current applications, commonly found in switching power supplies and motor control circuits. It possesses higher voltage and current handling capabilities compared to the BC547 and BC558. These ICs are selected for their compatibility with the circuit’s operating requirements and the anticipated load conditions.
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
- P1-P2 = 47K
- R1-R2 = 1K
- R3-R4 = 270R
- R5-R6 = 100R/1W
- R7-R8 = 22R/5W
- C1-C2 = 0.47uF
- Q1-Q2 = BC547
- Q3-Q4 = BC558
- Q5-Q6 = BD140
- Q7-Q8 = 2N3055
- SW1 = On-Off Switch
- T1 = 230V AC Primary 12-0-12V
- 4.5A Secondary Transformer
- B1 = 12V 7Ah