- Clap-Activated Relay Circuit: Diagram & Build Guide
- Room Noise Detector Circuit: Build Your dB Threshold!
- Build Your Own 1.8KHz Whistle Responder Circuit
- Whistle Responder Circuit: Build Your Own Beeping Gadget
- Voice Activated Switch: Mastering R6 for Superior VOX Control
- Build Your Key Finder: A 3-4kHz Circuit
- Room Noise Detector: Build Your dB Threshold Circuit
- Sound-Activated Relay Circuit: Build Your Responsive Project
- Whistle Circuit: Build a Toggle Flip-Flop with Filters
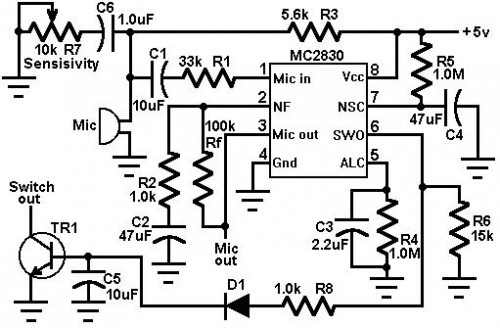
Voice Activated Switch: Mastering R6 for Superior VOX Control
Circuit diagram
A voice-activated switch (VOX) is implemented using an MC2830. Conventional VOX circuits frequently struggle to differentiate between spoken words and surrounding environmental sounds. Within a noisy atmosphere, the switch might be erroneously triggered by extraneous sounds, or the activation threshold must be lowered to achieve proper functionality. This design successfully addresses this limitation. It activates based on voice signal levels exceeding the background noise and does not respond to ambient sound. This functionality is achieved by exploiting the differences between voice and noise waveforms. Voice waveforms typically exhibit significant fluctuations in amplitude, while noise waveforms maintain a more consistent level. The sensitivity of the voice activation is influenced by the value of R6. A change from a 14kΩ resistor to a 7.0kΩ resistor in R6 reduces the voice activation sensitivity from 3.0dB to 8.0dB above the background noise.
Integrated Circuit Details
The MC2830 is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in audio and voice control applications. It's a comparator IC, designed to compare two analog input voltages and output a digital signal representing which input has the higher voltage. In this circuit, the MC2830 acts as the core component, constantly monitoring the incoming audio signal and the ambient noise level to determine whether to activate the voice-activated switch. It effectively converts the analog audio signals into a digital signal allowing for precise control of the switch based on voice level and noise characteristics. [/=h3]circuit from http://www.electronics-lab.com/