- Electronic Torricelli Barometer Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- Build Your 1.8-220V DC/AC Voltage Detector Circuit
- Build Your Pulse Generator: 1.5V Circuit Explorer
- Signal Tracer Injector Circuit: Fault Find Audio & Radio
- Build Your Own PIC Servo Tester Circuit Diagram
- Build Your dB Meter: 3-Level Sound Indicator
Build Your Pulse Generator: 1.5V Circuit Explorer
Simple test-instrument
Very basic circuitry, 1.5V Battery-powered
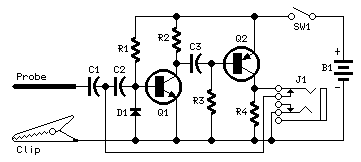
Circuit diagram
Parts:
- R1 1M 1/4W Resistor
- R2,R4 2.7K 1/4W Resistors
- R3 150K 1/4W Resistor
- C1 2.2nF 630V Ceramic or Polyester Capacitor (See Notes)
- C2,C3 4.7nF 63V Ceramic or Polyester Capacitors
- D1 1N4148 75V 150mA Diode
- Q1 BC547 45V 100mA NPN Transistor
- Q2 BC557 45V 100mA PNP Transistor
- SW1 SPST miniature Slider Switch (See Notes)
- J1 Stereo switched 3mm. Jack socket (See Notes)
- Probe Metal Probe 3 to 5 cm. long
- Clip Miniature Crocodile Clip
- B1 1.5V Battery (AA or AAA cell etc.)
Device purpose:
This uncomplicated circuit generates narrow pulses at approximately 700-800Hz frequency. The pulses, including harmonics up to the MHz region, can be injected into audio or radio-frequency stages of amplifiers, receivers, and similar devices for diagnostic purposes. A high-pitched tone can be heard from the speaker of the device under test when operation is correct. The clip must be connected to the ground of the device under test, making contact with the probe at various stages of the circuit, starting from the final stage and proceeding toward the initial one. When the tone vanishes, the defective stage has been identified.
Connecting an earclip or headphones to J1, the connection from Q2 Collector and C2-C3 is interrupted by the switch incorporated into J1: in this instance, the circuit converts into a two-stage amplifier and any audio signal emitted from the device under test and captured by the probe is reproduced through the headphones. The testing of a circuit ought to be carried out in the reverse manner, namely, commencing from the first stage and proceeding towards the final one. If nothing is heard, the defective stage has been found.
Circuit operation:
Q1 & Q2 form a complementary astable multivibrator, whose operating frequency is primarily determined by R3, C2 & C3 values. Output pulses are taken at Q2 Collector and applied to the probe via decoupling capacitor C1. D1 provides a symmetrical form for the output waveform.
More about components
The BC547 and BC557 are NPN and PNP bipolar junction transistors, respectively. These transistors act as switches and amplifiers in the circuit. Bipolar junction transistors are three-terminal semiconductor devices. They consist of a base, a collector, and an emitter. They are used to amplify or switch electronic signals. The transistors’ operating voltages (45V) and currents (100mA) are chosen to ensure sufficient performance within the circuit’s operating conditions.
Notes:
- If you intend to utilize the circuit for evaluating valve-operated devices, C1 must be a 630V type. When working with low voltage supply transistor devices, the voltage of C1 can be decreased to 63 or 100V.
- If instead of a short probe, you intend to connect the circuit to the device under test by means of a piece of wire longer than a few centimeters, a small ceramic capacitor (470 to 1000pF) should be added in parallel to D1 to prevent unwanted RF oscillation.
- Current drawing when in Pulse-Generator mode is approximately 60µA and 1.2mA when in Signal-Tracer mode operation. Therefore SW1 can be omitted, provided that the earclip or headphones are unplugged when the circuit is unused.
- J1 is a stereo switched jack socket wired to obtain a series connection of the two earpieces forming a stereo headphone. In this manner, the circuit is loaded with a higher impedance, and sensitivity will be improved.
- Therefore, the higher the load impedance, the more sensitive the Signal-Tracer. In any case, common 32 Ohm impedance mini-headphones suitable for walkman sets will work fine.
- A crystal (high impedance) earpiece is a good solution, provided you substitute J1 with a mono switched jack socket.
- The entire circuit can be easily fitted into a pen-like enclosure, with the probe protruding like a nib.
circuit from http://www.redcircuits.com/