similar circuits
- Build a 4-Stage Stabilised Power Supply with Short Circuit Protection
- Build Your Own 3-30V Adjustable DC Power Supply
- Build Your Own 9V 2A DC Power Supply Circuit
- Build Your Own: 1.3-22V Adjustable Power Supply Circuit
- Adjustable Current Limit: Dual Power Supply Design
- Build Your High-Performance 170V Hybrid Amplifier Power Supply
- Build Your 15V Regulated Power Supply Circuit – Simple & Powerful
- Transformerless 5V Power Supply Design Guide
- Build Your Own 24V 2A Variable DC Power Supply
- High Voltage Regulator: Design and Short Circuit Protection
- Boost Regulator Current: Design Your 1500mA Circuit
- Extend Smoke Alarm Battery Life with 12V Power
- 2 Watt Switching Power Supply: Build Your Own Circuit
- Variable Voltage & Current Power Supply: Build Your 0-3 Amp Circuit
- Build Your 24 Volt 3 Amp Power Supply Circuit
home :: power supply :: dc power supply :: build your 15v regulated power supply circuit – simple & powerful
Build Your 15V Regulated Power Supply Circuit – Simple & Powerful
Description
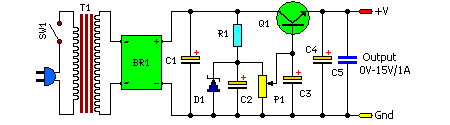
This power supply circuit is remarkably straightforward to construct, readily assembled onto a standard printed circuit board. Obtaining the necessary materials is uncomplicated, and the overall cost remains quite economical. The output voltage is consistently maintained and carefully controlled, operating within the range from 0V to +15V DC, with a maximum current capacity of 1A. This regulation is achieved through the utilization of P1. The Q1 component is a conventional power transistor and necessitates placement upon a heat sink; continuous operation at its highest current level results in elevated temperatures. The transformer employed is a commonly available model.Circuit diagram:
Parts:
- P1 = 330R Potentiometer
- R1 = 560R, 2W Resistor
- C1 = 2200uF, 35V Capacitor
- C2 = 100uF, 35V Capacitor
- C3 = 10uF, 25V Capacitor
- C4 = 220uF, 25V Capacitor
- C5 = 100nF, 63V Capacitor
- D1 = 18V, 1.5W Zener Diode
- Q1 = 2N3055 NPN Transistor
- T1 = 220VAC – 18V @ 1.5A Transformer
- BR1 = 4x1N4007 Diode Bridge
- SW1 = Mains On-Off Switch
More about components
The D1 component is a Zener diode, a crucial element for voltage regulation. Zener diodes are semiconductor diodes designed to operate in reverse breakdown region. When a reverse voltage exceeds the Zener voltage, the diode conducts current, providing a stable reference voltage. In this circuit, the 18V Zener diode acts as a reference point, ensuring a consistent voltage output despite variations in the input. Its main function is to provide a precise voltage level for the subsequent stages of the circuit. The diode is rated at 1.5W, indicating its power handling capacity.