similar circuits
- Protect Your Line: Building a Lightning Surge Shield
- Build a Telephone Ringer: Circuit & Control
- Cellular Phone Call Detector: Build Your Own Schematic
- Telephone Amplifier Circuit Diagram – Boost Your Voice!
- Build a Cell Phone Call Detector with Flashing LED
- Ringing Phone Light Flasher Circuit Diagram Build Guide
- Soft Musical Ringer Circuit Diagram: Build Your Own!
- Build a 48V Hold Music Circuit Diagram
home :: telephone related :: miscellaneous telephone :: build a cell phone call detector with flashing led
Build a Cell Phone Call Detector with Flashing LED
Illuminates an LED upon receiving an incoming call
It is powered by a single 1.5V cell
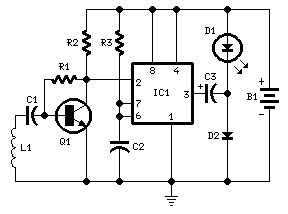
Circuit Diagram
Components:
- R1 100K 1/4W Resistor
- R2 3.9K 1/4W Resistor
- R3 1M 1/4W Resistor
- C1, C2 100nF 63V Polyester Capacitors
- C3 220µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- D1 Red LED 10mm. Ultra-bright (refer to the accompanying documentation)
- D2 1N5819 40V 1A Schottky-barrier Diode (see the supplementary information)
- Q1 BC547 45V 100mA NPN Transistor
- IC1 7555 or TS555CN CMOS Timer IC
- L1 Sensor coil (see the documentation)
- B1 1.5V Battery (AA or AAA cell, for instance)
Device Purpose:
This circuit has been engineered to detect incoming telephone calls (even if the call tone of the phone is muted) by triggering a flashing LED. The device should be positioned a few centimeters away from the cellular phone to enable the sensor coil L1 to perceive the electromagnetic field emanating from the phone's receiver during a call.
Circuit Operation:
The signal detected by the sensor coil is amplified by transistor Q1, subsequently driving the monostable input pin of IC1. The IC's output voltage is boosted by C2 & D2, allowing it to power the high-efficiency, ultra-bright LED at an appropriate peak voltage.
Supplementary Information:
- The current drawn in stand-by mode is less than 200µA; therefore, a power on/off switch is not required.
- The sensitivity of this circuit is influenced by the type of sensor coil used.
- L1 can be constructed by winding 130 to 150 turns of 0.2 mm enameled wire on a 5 cm diameter former (e.g., a can). Remove the coil from the former and wind it with insulating tape to create a self-contained coil.
- A commercially available 10mH miniature inductor, typically found in a small rectangular plastic casing, can be satisfactorily employed, although with somewhat reduced sensitivity.
- IC1 must be of a CMOS type; only these devices are suitable for operation at a 1.5V supply or lower voltage levels.
- Any Schottky-barrier type diode can be used in place of the 1N5819; the BAT46 is an excellent alternative.
author: RED Free Circuit Designs
circuit from http://www.redcircuits.com/
circuit from http://www.redcircuits.com/