- Simple 4 Transistor Hearing Aid Circuit Diagram
- Amplified Ear: Build a Sensitive Sound Amplifier
- Build Your Own 3V Hearing Aid Circuit Diagram
- Studio Stereo Headphone Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- Stereo Headphone Amplifier: Build Your 90mR Circuit
- 427mW Class-A Headphone Amp
- Portable Headphone Amp: Circuit & 3.7V Upgrade
- 100mW Headphone Amplifier Schematic Build Guide
- LME49830 High Power Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- TDA7052 Speech Amplifier Circuit Diagram & Build Guide
- DC-Coupled Audio Amplifier Design: A Practical Guide
- Build a Low-Power IR Audio Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- 8 Watt Audio Amplifier Schematic: Build Your Powerful Project
- 7 Watt TDA2003 Audio Amplifier Circuit Design
- High-Power 60W Audio Amplifier Schematic Design
Amplified Ear: Build a Sensitive Sound Amplifier
Description
This circuit, connected to 32 Ohm impedance mini-earphones, can detect very remote sounds. Useful for theatre, cinema and lecture goers: every word will be clearly heard. You can also listen to your television set at a very low volume, avoiding to bother relatives and neighbors. Even if you have a faultless hearing, you may discover unexpected sounds using this device: a remote bird twittering will seem very close to you.
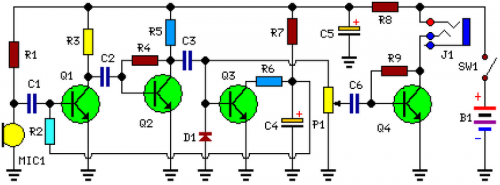
Circuit Diagram:
Parts:
- P1 = 22K
- R1 = 10K
- R2 = 1M
- R3 = 4K7
- R4 = 100K
- R5 = 3K9
- R6 = 1K5
- R7 = 100K
- R8 = 100R
- R9 = 10K
- C1 = 100nF 63V
- C2 = 100nF 63V
- C3 = 1µF 63V
- C4 = 10µF 25V
- C5 = 470µF 25V
- C6 = 1µF 63V
- D1 = 1N4148
- Q1 = BC547
- Q2 = BC547
- Q3 = BC547
- Q4 = BC337
- J1 = Stereo 3mm. Jack socket
- B1 = 1.5V Battery (AA or AAA cell etc.)
- SW1 = SPST Switch (Ganged with P1)
- MIC1 = Miniature electret microphone
Circuit Operation :
The core of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. All the signals picked-up by the microphone are amplified at a constant level of about 1 Volt peak to peak. In this manner very low amplitude audio signals are highly amplified and high amplitude ones are limited. This operation is accomplished by Q3, modifying the bias of Q1 (hence its AC gain) by means of R2. A noteworthy feature of this circuit is 1.5V battery operation. Typical current drawing: 7.5mA.
Notes:
- Due to the constant-volume control, some users may consider P1 volume control unnecessary. In most cases it can be omitted, connecting C6 to C3. In this case use a SPST slider or toggle switch as SW1.
- Please note the stereo output Jack socket (J1) connections: only the two inner connections are used, leaving open the external one. In this way the two earpieces are wired in series, allowing mono operation and optimum load impedance to Q4 (64 Ohm).
- Using suitable miniature components, this circuit can be enclosed in a very small box, provided by a clip and hanged on one’s clothes or slipped into a pocket.
- Gary Pechon from Canada reported that the Amplified Ear is so sensitive that he can hear a whisper 7 meters across the room.
- He hooked a small relay coil to the input and was able to locate power lines in his wall. He was also able to hear the neighbor’s stereo perfectly: he could pick up the signals sent to the speaker voice coil through a plaster wall.
- Gary suggests that this circuit could make also a good electronic stethoscope.
1N4148
The 1N4148 is a general-purpose diode, frequently used as a rectifier in power supplies or as a switching diode. It's a silicon diode with a typical forward voltage drop of 0.7V at a current of 1 Ampere. This component facilitates unidirectional current flow, effectively blocking current in one direction while allowing it to pass in the other. Its reliable performance makes it suitable for various circuit applications, providing both protection against reverse polarity and efficient current routing.
BC547
The BC547 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor. This transistor is commonly used in switching and amplification applications. It features a moderate gain and is often selected for its small size and readily available supply. The BC547's widespread use stems from its versatility and its performance characteristics, making it a popular choice in both amateur and professional electronics projects. Its performance is influenced by factors like temperature and bias conditions, which can be adjusted to optimize its operation for specific needs.
BC337
The BC337 is another common NPN bipolar junction transistor, favored for its relatively high current gain and moderate voltage rating. It's frequently found in applications requiring intermediate amplification or switching. This transistor is known for its predictable performance, making it a reliable choice in many electronic circuits. The BC337’s performance is influenced by factors like temperature and bias conditions, which can be adjusted to optimize its operation for specific needs. Because of its characteristics, it is often preferred in circuits demanding moderate power handling and robust performance under varying conditions.
circuit from http://www.extremecircuits.net/2009/06/amplified-ear_28.html