- Simple 4 Transistor Hearing Aid Circuit Diagram
- Amplified Ear: Build a Sensitive Sound Amplifier
- Build Your Own 3V Hearing Aid Circuit Diagram
- Studio Stereo Headphone Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- Stereo Headphone Amplifier: Build Your 90mR Circuit
- 427mW Class-A Headphone Amp
- Portable Headphone Amp: Circuit & 3.7V Upgrade
- 100mW Headphone Amplifier Schematic Build Guide
- LME49830 High Power Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- TDA7052 Speech Amplifier Circuit Diagram & Build Guide
- DC-Coupled Audio Amplifier Design: A Practical Guide
- Build a Low-Power IR Audio Amplifier Circuit Diagram
- 8 Watt Audio Amplifier Schematic: Build Your Powerful Project
- 7 Watt TDA2003 Audio Amplifier Circuit Design
- High-Power 60W Audio Amplifier Schematic Design
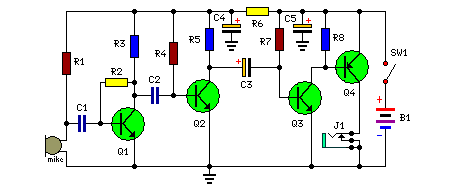
Simple 4 Transistor Hearing Aid Circuit Diagram
Description
High-end assistive listening devices can represent a significant financial investment. Here is a budget-friendly hearing aid circuit employing only four transistors and a selection of passive elements.
Circuit Diagram
Components:
- R1 = 2.2K
- R2 = 680K
- R3 = 3.3k
- R4 = 220K
- R5 = 1.5K
- R6 = 220R
- R7 = 100K
- R8 = 680K
- C1 = 104pF
- C2 = 104pF
- C3 = 1uF/10V
- C4 = 100uF/10V
- C5 = 100uF/10V
- Q1 = BC549
- Q2 = BC548
- Q3 = BC548
- Q4 = BC558
- J1 = Headphone jack
- B1 = 2x1.5V Cells
- SW1 = On/Off-Switch
Circuit Operation:
When the power switch SW1 is positioned in the ‘on’ configuration, the condenser microphone captures the auditory signal. This signal is then intensified by transistor Q1 and Q2. Subsequently, the enhanced signal is transmitted through coupling capacitor C3 to the base of transistor Q3.
Further amplification of the signal is achieved through transistor Q4, facilitating drive of a low-impedance earphone. Capacitors C4 and C5 function as power supply decoupling capacitors. The circuit is easily constructible on a small, general-purpose printed circuit board or a Vero board.
The device operates on a 3V DC power source. This can be accomplished utilizing two small 1.5V cells. The switch S should remain in the ‘off’ state when the circuit is not in active use. Improved sensitivity of the condenser microphone can be attained by enclosing it within a compact tube.
More about components
Transistors, such as the BC549, BC548, and BC558, are fundamental semiconductor components. These devices act as amplifiers and switches, controlling the flow of electrical current based on an applied input signal. They are widely utilized in electronic circuits for their ability to amplify weak signals and switch between conducting and non-conducting states. The BC549 is a general-purpose NPN transistor, frequently used in low-power applications, whereas the BC548 and BC558 are also NPN transistors commonly found in various electronic circuits due to their robust performance characteristics. Their precise operation relies on the principle of current amplification and switching, making them crucial building blocks for complex electronic systems.
circuit from http://www.extremecircuits.net/2009/07/hearing-aid.html