- Build Your Own Battery-Powered Night Lamp Circuit
- Build Your Own Ultra Bright LED Lamp Circuit
- Dual LED Pilot Light Circuit: Build Your Appliance Monitor
- Build Your Solar Lamp: PR4403 Circuit Diagram
- Multicolor LED Circuit for Disk Drive Status
- Mains LED Circuit: 100-240V AC Schematic
- Automatic Emergency Light Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- LED Torch Circuit Diagram: 80x Longer Battery Life
- Build Your Doorbell Warning Circuit: 22 Ohm Resistor Design
- Build a 120V Line-Powered White LED Circuit (2.4K Resistor)
- Build a 5V AC to LED Circuit with Safety
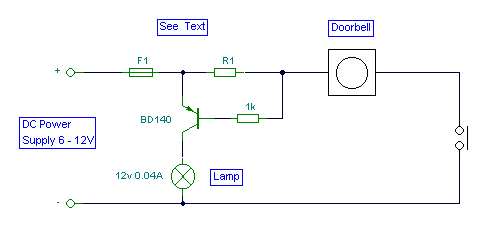
Build Your Doorbell Warning Circuit: 22 Ohm Resistor Design
Circuit Diagram
Significant Disclaimer:
This design is exclusively intended for use with solenoid-based chime doorbells; electronic models producing musical sequences are incompatible with this circuit.
Considerations:
- The most challenging aspect of this circuit was the naming convention. It’s often difficult to perceive the sound of a doorbell while watching television, and this circuit addresses this issue by offering a visual cue, namely, an illumination lamp. Alternatively, a light-emitting diode (LED) could also be utilized. Connecting a lamp in parallel across the doorbell would necessitate an additional load from the doorbell’s batteries or transformer. Incorporating a series resistor, R1, effectively minimizes current flow, consequently extending the operational lifespan of the batteries when powered by them. The value of R1 has been carefully selected to yield a voltage drop of approximately 0.6 to 0.7 volts across it, ensuring that the doorbell continues to function correctly. A combination of a 22-ohm resistor alongside a 50-ohm resistor was employed, resulting in proper operation of the circuit and a functioning doorbell.
Integrated Circuit Details
Resistors play a crucial role in electrical circuits, controlling the flow of current. A resistor, represented here by a 22-ohm value and a 50-ohm value, opposes the flow of electricity, preventing excessive current from damaging components. These resistors, typically constructed with materials like carbon or metal oxide film, demonstrate resistance measured in ohms. They are essential for voltage division, current limiting, and overall circuit stability. Their precise values are carefully chosen to achieve the desired circuit behavior. The use of multiple resistor values, as seen in this design, allows for fine-tuning of the circuit’s performance. The resistance of a resistor is denoted as R, measured in ohms (Ω).
Integrated Circuit Details
Integrated circuits (ICs), also known as microchips, are complex electronic circuits miniaturized onto a single semiconductor chip. They are the building blocks of modern electronics, integrating numerous transistors, resistors, and capacitors into a compact package. This design incorporates ICs – complex devices created by precisely arranging transistors on a silicon substrate. The use of ICs provides advantages such as reduced size, lower power consumption, and improved reliability compared to discrete components. These ICs, such as microcontrollers, amplify signals, perform calculations, and control other electronic circuits. Their complexity allows for the creation of sophisticated electronic systems. The presence of ICs contributes significantly to the functionality and efficiency of this circuit. These sophisticated devices contain millions of transistors that act as switches, controlling the flow of electrical current based on input signals, therefore controlling the circuit’s behavior.