- Build Your Own Battery-Powered Night Lamp Circuit
- Build Your Own Ultra Bright LED Lamp Circuit
- Dual LED Pilot Light Circuit: Build Your Appliance Monitor
- Build Your Solar Lamp: PR4403 Circuit Diagram
- Multicolor LED Circuit for Disk Drive Status
- Mains LED Circuit: 100-240V AC Schematic
- Automatic Emergency Light Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- LED Torch Circuit Diagram: 80x Longer Battery Life
- Build Your Doorbell Warning Circuit: 22 Ohm Resistor Design
- Build a 120V Line-Powered White LED Circuit (2.4K Resistor)
- Build a 5V AC to LED Circuit with Safety
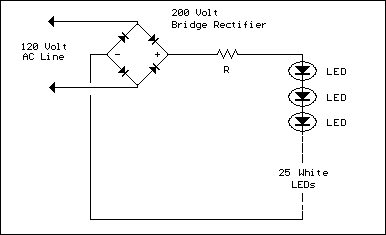
Build a 120V Line-Powered White LED Circuit (2.4K Resistor)
Description
The LED circuit below demonstrates the application of 25 white LEDs arranged in series, connected to the 120VAC line. Modifications can be made to increase or decrease the number of LEDs by adjusting the resistor value. The precise resistance will depend on the specific LEDs utilized. Calculating this resistance is somewhat complex due to the intermittent flow of current through the resistor. In operation, the output of the bridge rectifier is approximately 120 DC RMS or 170 volts peak. When employing 25 white LEDs with a typical forward voltage of 3 volts each, the total LED voltage amounts to 75 volts. The peak resistor voltage will be 170 - 75, resulting in 95 volts, although the resistor voltage is not continuous as the input must surpass 75 before current begins to flow. This “dead time” represents about 26 degrees of the 90-degree half-wave rectified cycle, (asin) 75/170 = (asin) .44 = 26 degrees. Consequently, the resistor will conduct for 90-26 = 64 degrees, or roughly 71 percent of the time.
Next, the peak LED current can be determined to calculate the resistor value. Assuming an LED current of 20mA RMS, the peak current will be 20*1.414 or 28mA. However, given the duty cycle is only 71 percent, this figure needs to be increased to 28/0.71 = 39mA. Therefore, the resistor value should be 95/.039 = 2436 ohms (2.4K) and the power rating will be .02^2 *2400= .96 watts. A two watt size is recommended.
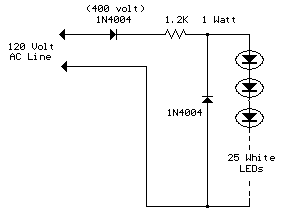
Furthermore, this circuit can be constructed utilizing two diodes and a resistor, as illustrated in the lower drawing. The second diode in parallel with the LEDs is implemented to avoid a reverse voltage on the LEDs should the other diode exhibit a slight leakage. While potentially unnecessary, it was considered a prudent measure.
Calculating the resistor value follows a similar process to the previous example, yielding a value approximately half that of the full-wave version, or approximately 1.2K at 1 watt in this case. The peak LED current will be doubled, or about 78mA. This is generally acceptable, but it’s advisable to consult the maximum current specifications for short-duty-cycle LEDs when utilized and verify that 79mA doesn’t exceed these limits.