- Build a 4-Stage Stabilised Power Supply with Short Circuit Protection
- Build Your Own 3-30V Adjustable DC Power Supply
- Build Your Own 9V 2A DC Power Supply Circuit
- Build Your Own: 1.3-22V Adjustable Power Supply Circuit
- Adjustable Current Limit: Dual Power Supply Design
- Build Your High-Performance 170V Hybrid Amplifier Power Supply
- Build Your 15V Regulated Power Supply Circuit – Simple & Powerful
- Transformerless 5V Power Supply Design Guide
- Build Your Own 24V 2A Variable DC Power Supply
- High Voltage Regulator: Design and Short Circuit Protection
- Boost Regulator Current: Design Your 1500mA Circuit
- Extend Smoke Alarm Battery Life with 12V Power
- 2 Watt Switching Power Supply: Build Your Own Circuit
- Variable Voltage & Current Power Supply: Build Your 0-3 Amp Circuit
- Build Your 24 Volt 3 Amp Power Supply Circuit
Build Your Own High Current Power Supply Circuit
Description
Following the initial publication of this webpage, numerous inquiries regarding a robust current-providing power supply were received. After a thorough investigation, a suitable solution was developed. This design represents a linear supply, although it may elicit some skepticism, it incorporates a minimal number of components, is straightforward to assemble, and is capable of delivering substantial currents.
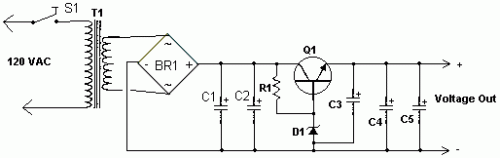
Circuit Diagram
Components
- R1 680 Ohm 1/4 Watt Resistor
- C1 20,000 - 50,000uF 20-40 Volt Capacitor
- C2, C3 100uF 50 Volt Capacitor
- C4 0.1uF 50 Volt Capacitor
- C5 0.01uF 50 Volt Capacitor
- D1 Zener Diode (Refer to accompanying notes)
- Q1 2N3055 Or Equivalent (See Notes)
- T1 Transformer (See Notes)
- BR1 Bridge Rectifier (See Notes)
- S1 SPST 250 VAC 10 A Switch
- MISC Case, Line Cord, Heatsink For Q1, Binding Posts For Output
Notes
- D1 must be specified with a voltage rating approximately one volt greater than the desired output of the supply. A 1/2 watt diode will suffice.
- Q1 can be a transistor similar to the 2N3055. The 2N3055 was chosen for its availability and high power handling capacity (150 watts).
- T1 should have a voltage rating roughly five volts above the desired output voltage, and a current rating about one amp higher. This voltage buffer is required by the regulation section, and the increased current is to prevent overheating of the transformer.
- The selection of BR1 will depend on the voltage and current capabilities of your transformer. The rectifier should be rated for 50 volts more than the transformer, and 5 amps more than the transformer.
- The value of R1 may be reduced when supplying larger currents. Experimentation is encouraged until the desired outcome is achieved.
- Adequate heat dissipation is absolutely crucial; utilize a heatsink and fan for optimal performance!
Zener Diode
A Zener diode, designated as D1, plays a crucial role in regulating the output voltage of the supply. This diode, typically rated at approximately one volt higher than the target supply voltage, acts as a voltage reference point. The diode ensures a stable output, preventing fluctuations and maintaining a consistent voltage level. A 1/2 watt diode is usually sufficient for this application. It is important to select a Zener diode with the right characteristics for this circuit.
Transistor
The transistor, denoted as Q1, functions as a switching device within the linear power supply design. As a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), it controls the flow of current, providing amplification and acting as the core of the regulation circuit. The 2N3055 is often utilized due to its widespread availability and robust power handling capacity of 150 watts. This ensures the circuit operates reliably under high-current conditions. The transistor's properties are crucial for the proper functionality of the circuit. Selecting the right transistor is a key step in building the circuit.