- Build a 4-Stage Stabilised Power Supply with Short Circuit Protection
- Build Your Own 3-30V Adjustable DC Power Supply
- Build Your Own 9V 2A DC Power Supply Circuit
- Build Your Own: 1.3-22V Adjustable Power Supply Circuit
- Adjustable Current Limit: Dual Power Supply Design
- Build Your High-Performance 170V Hybrid Amplifier Power Supply
- Build Your 15V Regulated Power Supply Circuit – Simple & Powerful
- Transformerless 5V Power Supply Design Guide
- Build Your Own 24V 2A Variable DC Power Supply
- High Voltage Regulator: Design and Short Circuit Protection
- Boost Regulator Current: Design Your 1500mA Circuit
- Extend Smoke Alarm Battery Life with 12V Power
- 2 Watt Switching Power Supply: Build Your Own Circuit
- Variable Voltage & Current Power Supply: Build Your 0-3 Amp Circuit
- Build Your 24 Volt 3 Amp Power Supply Circuit
Transformerless Power Supply: Simple Circuit Design
Description
Several inquiries have been submitted requesting a design for a transformerless power supply. Herein is a particular example of such a supply. This design avoids the use of a substantial step-down transformer and boasts a remarkably low number of components. The circuit can be constructed at a compact size and is suitable for powering small-scale projects. However, a significant limitation of this supply is the absence of electrical isolation from the alternating current (AC) line, restricting the maximum current it can deliver.
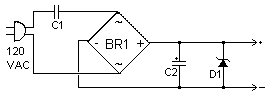
Circuit diagram
Parts:
- C1 0.39uF 250V Capacitor
- C2 220uF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- D1 1N4741 11V Zener Diode (See Notes)
- BR1 1 Amp 200V Bridge Rectifier
- MISC Line Cord, Board, Wire, Case
Notes:
- The value of C1 can be increased to enhance the current output of the circuit. Utilizing the specified values, the circuit is capable of delivering approximately 15mA. It is necessary to proportionally adjust the size of C2.
- Alternative values can be utilized for D1 to modify the voltage levels as required.
- It is essential to acknowledge that this circuit lacks electrical isolation from 120VAC. Consequently, meticulous caution must be exercised, and the circuit must be enclosed at all times. Work on the circuit (or any other circuits connected to it) should never be performed while it is connected to the power source.
- Adding a resistor in series with C1 is recommended to limit the current flow if the circuit is energized at full mains voltage.
- When operating the circuit from 220VAC, a capacitor with a rating exceeding 400V should be employed for C1.
- For the purpose of achieving electrical isolation from the AC line, a small isolation transformer can be incorporated at the circuit’s inputs. 600ohm:600ohm audio transformers can be utilized effectively.
More about components
Integrated circuits (ICs) play a crucial role in modern electronic designs, offering compact and efficient solutions for complex functions. These components, often referred to as microchips, integrate numerous transistors, resistors, and capacitors onto a single silicon chip. They are fundamental building blocks in a vast array of applications, from low-power signal processing to high-speed logic. The 1N4741 diode, for example, is a silicon zener diode that is commonly used to provide protection for circuits against excessive voltage. Its primary function is to regulate voltage levels and prevent damage to other components. Furthermore, Zener diodes are frequently employed in voltage clipping applications, limiting the maximum voltage a circuit can experience. This is crucial for protecting sensitive electronics from overvoltage conditions. The consistent and reliable performance of these ICs makes them a vital part of countless electronic designs, contributing to the efficient and reliable operation of numerous devices.