similar circuits
- 9V FM Transmitter Circuit: Build Your 100m Range
- Opamp VHF FM Transmitter Design (88-108 MHz)
- Build Your Own 50m Stereo Wireless Audio Link Circuit
- FM 45W Valve Transmitter Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- Build Your Own 85-108 MHz Radio Transmitter!
- 3W FM Transmitter Schematic Blueprint
- Build Your Own 2 Transistor FM Voice Transmitter Circuit
- Build Your 88-108MHz 4W FM Transmitter Circuit
- FM Transmitter Bug: 4 Turns, 1.5 Turns – Build Your Circuit
- Build Your Own 98 MHz FM Beacon Transmitter
Build Your Own 2 Transistor FM Voice Transmitter Circuit
Caution: Exercise extreme care when working with transmitting circuits. Operating radio transmitters without the necessary authorization is unlawful in numerous nations. Despite employing low power levels, this particular circuit could potentially be adjusted to operate within the 87-108MHz frequency range, covering distances of 20 or 30 meters.
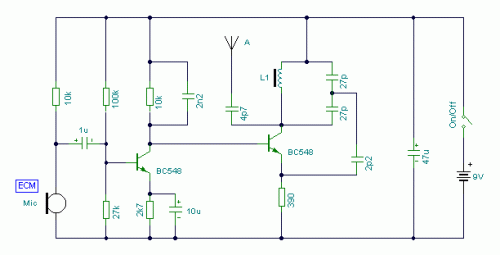
Circuit Diagram
Notes:
- A pair of BC548 transistors have been incorporated into this circuit design. While not specifically designed for radio frequency applications, they still produce satisfactory results. An ECM Mic insert, sourced from Maplin Electronics with order code FS43W, has been utilized. This two-terminal ECM offers precise signal reception. Alternatively, standard dynamic mic inserts can be implemented by simply removing the 10k resistor from the front. The coil L1, also obtained from Maplin with part number UF68Y, comprises seven turns wound around a quarter-inch plastic former, incorporating a tuning slug for fine adjustments. The tuning slug is crucial for adjusting the transmitter’s frequency. The observed operational range on the prototype varied from 70MHz to approximately 120MHz. The aerial consists of a few inches of wire. It is important to note that wires exceeding 2 feet in length can negatively impact the circuit’s performance by dampening oscillations and potentially preventing proper operation. Although RF circuits are typically built on a printed circuit board (PCB), veroboard can be utilized as a substitute; however, maintain all lead lengths as short as possible and strategically break tracks to ensure optimal performance.
author: Andy Collinson, anc@mitedu.freeserve.co.uk
circuit from http://www.zen22142.zen.co.uk/
circuit from http://www.zen22142.zen.co.uk/