- Long Delay Timer Circuit: 35 Minute Battery-Powered Design
- Build Your Custom 3-9 Minute Beep Timer Circuit
- Build Your Amplifier Timer Circuit – 15 Minute Delay
- Timed Beeper Circuit: Build Your Precise Timer!
- Build Your 30-Minute Bedside Lamp Timer Circuit
- Time Delay Circuit: Build Your Appliance Protector
- Midnight Security Light Circuit: A 1:00 AM Intrusion Defense
- Delay Relay Circuit: 12V, 15s
- Build a Powerful 1300W Space Heater Circuit Diagram
- Building a 1-Second Delayed Pulse with the 555 Timer
- 555 Timer Mono Stable Circuit Design & Build Guide
- Build Precise Time Delays with a 12-Stage Binary Counter
- Time Delay Circuit: 5A Output from Low Voltage Batteries
- Build a Powerful 1300W AC Heater Circuit Design
- Build Your 9-Second LED Timer & Relay Circuit 9V
Build a Powerful 1300W AC Heater Circuit Design
Description
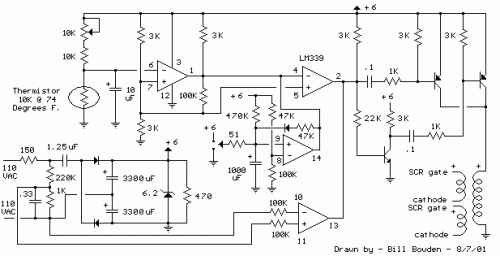
Below is a thermostat circuit recently constructed to manage a 1300 watt space heater. The heating element (not shown) is arranged in series with two back-to-back 16 amp Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs) (not shown), which are controlled by a small pulse transformer. The pulse transformer features three identical windings – two of which supply trigger pulses to the SCRs, and the third winding is connected to a PNP transistor pair that alternately provides pulses to the transformer at the beginning of each AC half cycle. The trigger pulses are applied to both SCRs near the beginning of each AC half cycle, but only one conducts depending on the AC polarity.
DC power for the circuit is depicted in the lower left section of the diagram and utilizes a 1.25uF, 400 volt non-polarized capacitor to generate approximately 50mA of current from the AC line. The current is rectified by two diodes and employed to charge a couple of larger low voltage capacitors (3300uF) which deliver approximately 6 volts DC for the circuit. The DC voltage is regulated by the 6.2 volt zener and the 150 ohm resistor in series with the line to limit the surge current when power is initially applied.
Integrated Circuits utilized in this circuit are the 6.2V zener diode and the 150 ohm resistor. The zener diode provides a stable reference voltage, ensuring consistent regulation of the DC power supply. The 150 ohm resistor acts as a current-limiting device, preventing excessive current flow during the initial power-up sequence, thereby safeguarding the circuit components. These are standard components used for voltage stabilization and current limiting respectively, commonly found in electronic circuits to protect against overvoltage or excessive current conditions.
The comparator near the center of the drawing (pins 8,9,14) is employed to enable the heater to be manually activated for a few minutes and automatically deactivate. A momentary toggle switch (shown connected to a 51 ohm resistor) is used to discharge the 1000uF capacitor so that pin 2 of the upper comparator moves to an open circuit state allowing the 60 Hz square wave to trigger the SCRs and power the heater. When the capacitor reaches approximately 4 volts the circuit returns to normal operation where the thermistor controls the operation. The momentary switch can also be toggled so that the capacitor charges above 4 volts and shuts off the heater if the temperature is above the setting of the pot.
The comparator at the center of the drawing (pins 8,9,14) functions as a manual override, providing a short-term heating capability. The use of a momentary switch coupled with a discharge capacitor allows for a manual operation. The capacitor, when charged, enables the 60 Hz square wave to activate the SCRs, and when discharged, returns the circuit to its normal thermistor-controlled state. This feature offers flexibility for temporary heating needs or for troubleshooting.
The lower comparator (output at pin 13) serves as a zero crossing detector and produces a 60 Hz square wave in phase with the AC line. The phase is shifted slightly by the 0.33 uF, 220K and 1K network so that the SCR trigger pulse arrives when the line voltage is a few volts above or below zero. The SCRs will not trigger at exactly zero since there will be no voltage to maintain conduction.
The upper two comparators operate in the same manner as described in the "Electronic thermostat and relay" circuit. A low level at pin 2 is produced when the temperature is above the desired level and inhibits the square wave at pin 13 and prevents triggering of the SCRs. When the temperature drops below the desired level, pin 2 will move to an open circuit condition allowing the square wave at pin 13 to trigger the SCRs.
The comparator near the center of the drawing (pins 8,9,14) is used to allow the heater to be manually run for a few minutes and automatically shut off. A momentary toggle switch (shown connected to a 51 ohm resistor) is used to discharge the 1000uF capacitor so that pin 2 of the upper comparator moves to a open circuit state allowing the 60 Hz square wave to trigger the SCRs and power the heater. When the capacitor reaches about 4 volts the circuit returns to normal operation where the thermistor controls the operation. The momentary switch can also be toggled so that the capacitor charges above 4 volts and shuts off the heater if the temperature is above the setting of the pot.