- Long Delay Timer Circuit: 35 Minute Battery-Powered Design
- Build Your Custom 3-9 Minute Beep Timer Circuit
- Build Your Amplifier Timer Circuit – 15 Minute Delay
- Timed Beeper Circuit: Build Your Precise Timer!
- Build Your 30-Minute Bedside Lamp Timer Circuit
- Time Delay Circuit: Build Your Appliance Protector
- Midnight Security Light Circuit: A 1:00 AM Intrusion Defense
- Delay Relay Circuit: 12V, 15s
- Build a Powerful 1300W Space Heater Circuit Diagram
- Building a 1-Second Delayed Pulse with the 555 Timer
- 555 Timer Mono Stable Circuit Design & Build Guide
- Build Precise Time Delays with a 12-Stage Binary Counter
- Time Delay Circuit: 5A Output from Low Voltage Batteries
- Build a Powerful 1300W AC Heater Circuit Design
- Build Your 9-Second LED Timer & Relay Circuit 9V
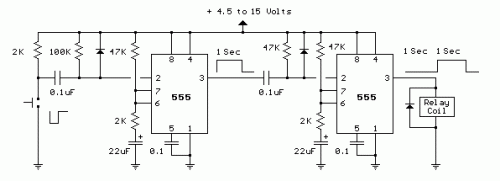
Building a 1-Second Delayed Pulse with the 555 Timer
Description
The diagram below showcases the production of a single positive signal, with a delay applied compared to the initiating input timing. This design mirrors the prior illustration but incorporates two operational phases, allowing for independent adjustment of both the pulse breadth and the delay duration. Upon pressing the button, the output of the initial stage will rise and maintain proximity to the power supply voltage until the predetermined delay time is completed, which is approximately 1 second. The second 555 timer instance remains inactive due to its need for a descending voltage at pin 2, ensuring that the second stage’s output remains low and the relay remains unpowered. At the conclusion of this delay period, the output of the first stage returns to a low level, and the falling voltage triggers the second stage’s output cycle, also lasting about 1 second as depicted.Circuit diagram
"The circuit utilizes a 555 timer IC, a versatile integrated circuit. This chip is a common, low-cost option frequently employed in timing applications. The 555 timer is a monolithic integrated circuit containing a comparator, a 555 timer, and a power supply. It is widely used for generating waveforms such as pulses, oscillations, and timers. Its operation relies on switching between three modes of operation: normal operation, astable mode, and monostable mode. The 555 timer IC operates by switching between these modes depending on the voltage at its control input. Its pin configuration includes pins for power supply (VCC and GND), output (OUT), trigger (TRIGGER), reset (RESET), and control voltage (CONTROL VOLTAGE). The IC is designed for ease of use and is frequently found in hobbyist and professional electronics projects.