- Boost Your MP3 Power: 32 Ohm Amplifier Circuit
- Build Your 9V Bass Booster Circuit Diagram
- Build Your 20dB Audio Booster Circuit Diagram
- Symmetrical Class A Preamplifier – Build Your Audio Masterpiece
- Build Your Perfect Symmetrical 4 Channel Amplifier Circuit
- Build Your Ideal Buffer: Class A Circuit Diagram (560Ω)
- Discrete Preamplifier Circuit Diagram
- Build Your Own: Microphone Preamplifier Circuit (2mA)
- Stereo Preamplifier Circuit: Build Your +16dB Bass Boost
- Phono Preamplifier Circuit Diagram: 47K, 6.8K, 47nF Build!
- Modular Preamplifier Switching Center: Build Your Stereo Chain
- Portable Microphone Preamplifier Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- Build Your Own Phono Preamplifier Circuit (18V)
- Amplify Signals: 741 Op-Amp Stethoscope Circuit Diagram
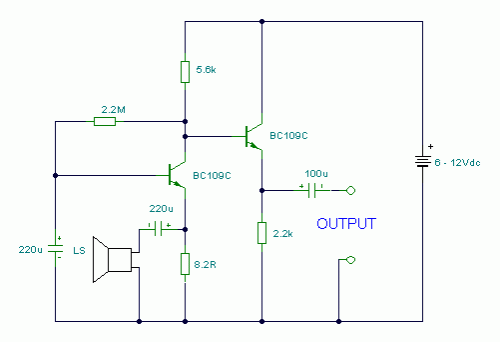
- Turn Speaker into Microphone: Build Your 6-12V Circuit
Turn Speaker into Microphone: Build Your 6-12V Circuit
Description:
This circuit transforms a standard loudspeaker into a functional reverse device, enabling its utilization as a microphone.
Circuit diagram
Notes:
This circuit facilitates the conversion of a readily available loudspeaker into a microphone. Acoustic waves impacting the speaker diaphragm generate variations within the voice coil. The movement of the voice coil within the speaker’s magnetic field then produces a weak electrical signal. The circuit is intended for operation with a DC voltage ranging from 6 to 12 volts. The initial transistor is configured in common-base mode, which optimizes the match between the loudspeaker’s low input resistance and the common-base stage while simultaneously providing significant voltage amplification. The subsequent stage is directly coupled and functions as an emitter follower. Although the voltage gain is marginally below 1, the output impedance remains low, effectively accommodating extended cable lengths.
Audio fidelity is somewhat inferior to that of a conventional or electret condenser microphone; however, serviceable outcomes can be achieved. Speaker cones with diameters ranging from 1 inch to 3 inches can be implemented. The speaker impedance may vary between 4 ohm and 64 ohm. The 8.2 ohm resistor value may be adjusted to align with the inherent impedance of the particular speaker being utilized.
Integrated Circuits:
Integrated circuits play a crucial role in this circuit’s operation. Specifically, transistors are employed as active components to manage and amplify the electrical signal generated by the loudspeaker. Transistors, a fundamental building block of modern electronics, are semiconductor devices that control the flow of current. They’re often used as switches or amplifiers, offering precise control and efficient signal processing. These components are carefully selected to optimize the circuit’s performance, offering a balance between amplification strength and impedance matching. The transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device, which acts as an electronic switch or amplifier. The transistor is a widely used component in electronic devices because of its small size and versatility. The use of transistors allows for efficient signal amplification and switching, contributing to the circuit's functionality.
circuit from http://www.zen22142.zen.co.uk/