- Build Your Dynamic LED Rhythm Circuit
- Dark Activated LED Flasher: Bowes Circuit Design
- Build a Stunning Two LED Flashing Circuit with Potentiometers
- Electronic Dice: Build Your Own Random Number Generator!
- Build a Rotating Back Light: 555 Timer Circuit Diagram
- Flashing Lamps Circuit: 230V AC with SCR Timing
- Portable 230V AC Lamp Flasher Circuit Diagram
- Build Your 4017 Decade Counter – A Brilliant 9-Step Sequence
- Build Your Own Flashing Lamp Circuit – 10W LED Support
- Pulsating LED Circuit: Build Your 4s Cycle Effect
- High-Intensity LED Flasher Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- Build a Reactive LED Circuit: Diagram & Parts List
- Pulse LED Circuit: Build a Dynamic Two-Strip Design
- 12 Stage Neon Sequencer: Circuit Diagram & Build Guide
- Flash Lamp Circuit: Build Your Own Flasher
Flash Lamp Circuit: Build Your Own Flasher
This collection of circuit diagrams is ideal for applications requiring continuous illumination from existing lamps.
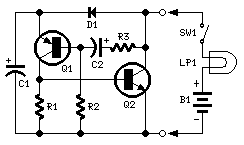
Circuit Diagram
Components:
- R1 6.8k Ohm 0.25W Resistor
- R2 270k Ohm 0.25W Resistor
- R3 22k Ohm 0.25W Resistor
- C1 220µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- C2 10µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- D1 1N4002 100V 1A Diode
- Q1 BC557 45V 100mA PNP Transistor
- Q2 BD139 80V 1.5A NPN Transistor
- LP1 Existing filament Lamp: any type in the range 3-24V 10W maximum.
- SW1 Existing On-Off switch
- B1 Existing V DC source: any type in the range 3-24V
- Suitable for the lamp adopted
Device Objective:
This circuit design is specifically created to transform lamps already incorporated within a system into flashing lights. Insertion of the circuit between the lamp’s connection and the negative power source is all that is needed. It is particularly well-suited for automotive or panel indicator lights, and it can support lamps consuming up to 10 Watts.
Important Considerations:
- Disconnect the lamp(s) from the negative supply connection(s) first, followed by the insertion of the circuit between the lamp connections and the negative supply, ensuring correct polarity!
- The value of C1 can be adjusted from 100 to 1000µF or higher to modify the flashing frequency.
- Although the components are larger than required, this circuit can also operate any LED, provided a resistor is connected in series with the light-emitting device.
- The resistor should be chosen within the range of 47R to 2.2kΩ, based on the supply voltage.
More about components
The BC557 and BD139 are NPN and PNP transistors, respectively. Transistors are fundamental semiconductor devices that act as electronic switches or amplifiers. The BC557 is a general-purpose NPN transistor commonly used in switching and amplification applications. Its key characteristics include a relatively high current gain, making it suitable for a wide range of signal amplification tasks. The BD139 is a PNP transistor known for its robust performance and versatility. It's frequently employed in circuits where a PNP transistor is required, and its higher voltage and current ratings make it suitable for demanding applications. Both transistors operate in the active region, where they can amplify weak signals or switch circuits on and off based on the input current. Proper selection of these transistors is essential for achieving optimal circuit performance and reliability.
circuit from http://www.redcircuits.com/