- Build Your Dynamic LED Rhythm Circuit
- Dark Activated LED Flasher: Bowes Circuit Design
- Build a Stunning Two LED Flashing Circuit with Potentiometers
- Electronic Dice: Build Your Own Random Number Generator!
- Build a Rotating Back Light: 555 Timer Circuit Diagram
- Flashing Lamps Circuit: 230V AC with SCR Timing
- Portable 230V AC Lamp Flasher Circuit Diagram
- Build Your 4017 Decade Counter – A Brilliant 9-Step Sequence
- Build Your Own Flashing Lamp Circuit – 10W LED Support
- Pulsating LED Circuit: Build Your 4s Cycle Effect
- High-Intensity LED Flasher Circuit Diagram – Build Your Own!
- Build a Reactive LED Circuit: Diagram & Parts List
- Pulse LED Circuit: Build a Dynamic Two-Strip Design
- 12 Stage Neon Sequencer: Circuit Diagram & Build Guide
- Flash Lamp Circuit: Build Your Own Flasher
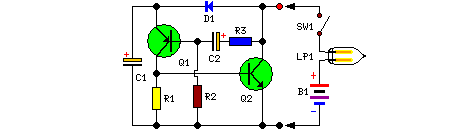
Build Your Own Flashing Lamp Circuit – 10W LED Support
Description
This circuit was developed to generate a pulsating effect in existing lamp installations, causing the lamps to flash continuously. It’s particularly well-suited for automotive or panel indicator lights, capable of powering lamps up to 10W. The device is implemented by placing it in the path between the lamp and the negative power source, ensuring correct polarity connections are maintained.
Circuit Diagram:
Parts:
- R1 = 6.8K
- R2 = 270K
- R3 = 220K
- D1 = 1N4002
- C1 = 220uF-25V
- C2 = 10uF-25V
- Q1 = BC557
- Q2 = BD139
- B1 = Any type within the 3-24V range
- B2 = Selected to match the connected lamp
- LP1 = Filament Lamp - 10W, operating from 3V to 24V
- SW1 = On-Off Switch
Notes:
- Disconnect the lamp from the negative supply connection and subsequently introduce the circuit between the lamp’s connection and the negative supply, adhering strictly to polarity requirements!
- The value of C1 can be altered between 100µF and 1000µF or even higher to adjust the flashing frequency.
- Despite its relatively large size, this circuit can also operate any LED, provided a suitable resistor is incorporated in series with the light-emitting device.
- This resistor should fall within the 47R to 2.2K2 range, depending on the supply voltage utilized.
More about components
Integrated circuits, or ICs, play a crucial role in this circuit’s functionality. Specifically, the BC557 and BD139 transistors act as switching elements, controlling the flow of current to create the pulsating effect. The BC557 is a general-purpose NPN transistor commonly used for switching and amplification, while the BD139 is a high-current NPN transistor suitable for driving inductive loads such as lamps. These transistors are fundamental to the circuit’s operation, enabling the controlled switching that produces the desired flashing effect. These ICs are commonly used in a range of electronic circuits, offering advantages like compactness, reliability, and low power consumption. They are frequently employed in switching applications, signal amplification, and logic gate implementation, contributing to their versatility and widespread use in various electronic systems.