- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
Description
Safeguard your valuable batteries from damage caused by excessive discharge with this compact electronic cutoff switch. It consumes minimal power and can be configured to suit a diverse range of battery voltages.
Main Features
- Disconnects the load at a predetermined battery voltage
- Automatically reconnects the load upon battery recharge
- Extremely low current consumption (<20ma)
- Small dimensions
- Maximum rating of 10A
- Suitable for use with 4.8-12.5V batteries
- Optional transient voltage protection
Suitable for use in...
- Vehicles, boats & recreational vehicles
- Security systems
- Emergency lighting
- Small solar power installations
- Camera battery packs
- Numerous other low-power applications
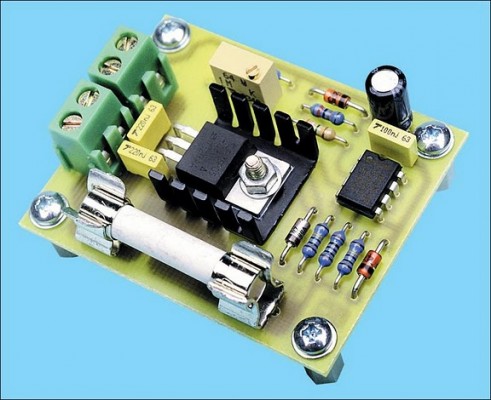
Picture of the project:
In May 2002, we (Silicon Chip) presented the “Battery Guardian”, a project specifically designed to protect 12V car batteries from deep discharge. This unit has gained significant popularity and remains available from kit suppliers. This revised design does not replace the Battery Guardian – particularly when applied to 12V car batteries. Instead, it offers a more adaptable alternative that can be utilized with a wide spectrum of battery voltages.
Parts layout:
This new “Micropower Battery Protector” has eliminated the low-battery warning circuitry and the relatively inexpensive N-channel MOSFET utilized in the Battery Guardian, in favor of a more diminutive module that draws considerably less battery power. It represents a slightly higher initial investment, but it can switch lower voltages, allowing it to be employed with 6V & 12V lead-acid batteries and 4-cell to 10-cell NiCd and NiMH battery packs.
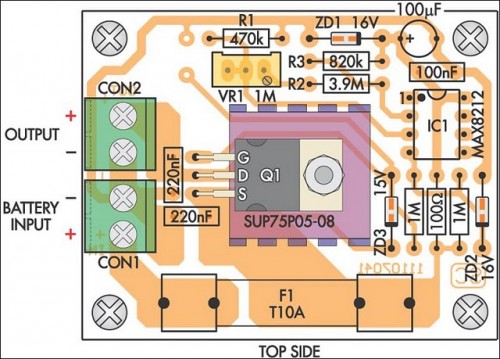
PCB layout:
Most battery-powered equipment lacks a mechanism for disconnecting the batteries when they are depleted. Even when the voltage drops below the normal operational threshold, battery drain frequently continues until all available energy is exhausted. This is especially prevalent in equipment designed to be powered by alkaline or carbon cells but subsequently modified with rechargeable batteries.
Circuit diagram:
An illustrative example includes emergency lighting and security equipment designed for float-charging from the mains. During an extended power outage, these batteries can be completely drained and may not recover when mains power is finally restored.