- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
Description
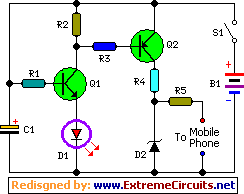
This document presents an effective portable charger utilizing 1.5 volt pen cells to recharge mobile devices during travel. It has the capability to restore a mobile phone’s battery three to four times in situations lacking alternating current power. Typical mobile phone batteries are specified to operate at 3.6 V/500 mA. A single pen torch cell provides 1.5 volts and 1.5 Amperes of current. Consequently, connecting four pen cells in a series configuration produces a battery pack delivering 6 volts and 1.5 Amperes. Activation of the circuit through S1 causes transistor Q1 to conduct, resulting in the illumination of the Green LED.
Upon conduction of Q1, Q2 also conducts due to the negative voltage applied to its base. Charging current is drawn from the collector of Q1. A 4.7 volt Zener diode D2 is employed to decrease the output voltage to 20 milliamperes for a slower charging rate. If a higher current is desired for expedited charging, the value of R4 can be reduced to 47 ohms, thereby generating an 80 milliampere current. The output terminals are designed for connection with the mobile phone; careful selection of pins and adherence to correct polarity are essential. This circuit originated from the provided source.
Circuit Diagram:
Parts:
- R1 = 1K
- R2 = 470R
- R3 = 4.7K
- R4 = 270R
- R5 = 27R
- C1 = 100uF-25V
- D1 = Green LED
- D2 = 4.7V/1W Zener Diode
- B1 = 1.5Vx4 Cells
- S1 = On/Off Switch
- Q1 = BC548
- Q2 = SK100
More about components
Transistors, such as the BC548 (Q1) and SK100 (Q2), are fundamental semiconductor devices. These components act as amplifiers and switches, controlling the flow of current based on input signals. The BC548 is a general-purpose NPN transistor often used in switching circuits, while the SK100 is a silicon NPN transistor known for its low saturation voltage. Their operation relies on the controlled movement of charge carriers – electrons – within the semiconductor material, enabling the circuit to perform switching and amplification functions. These integrated circuits are essential for efficient operation of this charging circuit.
Zener Diode
A Zener diode, specifically the 4.7V/1W model (D2), is a special type of diode that exhibits a predictable current-voltage relationship when reverse-biased. When a sufficient reverse voltage is applied, the diode will conduct current to maintain a constant voltage across it. In this circuit, the Zener diode is utilized to regulate the output voltage, ensuring that it remains at a stable 4.7 volts, which is suitable for charging the mobile phone battery. Its inherent ability to maintain a constant voltage is crucial for preventing overcharging and potential damage to the device being charged. This component safeguards the charging process by providing a controlled voltage source.