- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
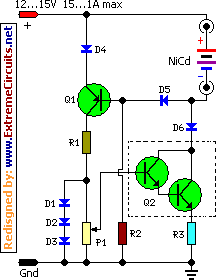
Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
Description
This NiCd battery Charger is capable of charging up to 7 NiCd batteries arranged in a series configuration. The capacity can be augmented by adding supplementary batteries, with an additional 1.65V supplied per supplementary battery. Provided Q2 is mounted on an appropriate heatsink, the input voltage can be elevated to a maximum of 25V. Notably, this charger distinguishes itself from many commercially available NiCd chargers by incorporating reverse polarity protection. Furthermore, it prevents battery discharge if the connection to the power supply is interrupted.
Typically, NiCd batteries require charging within approximately 14 hours, utilizing a charging current equal to one-tenth of their capacity. For instance, a 500 mAh battery would be charged at 50 mA over a period of 14 hours. Excessively high charging currents can detrimentally impact battery health. The charging current level is regulated by P1, spanning a range of 0 mA to 1000 mA. Q1 is deactivated when the NiCd battery is connected with the correct polarity or when the output terminals are devoid of connection. Q2 must be affixed to a heatsink. Should a BD679 be unavailable, it can be replaced with any NPN medium-power Darlington transistor possessing output specifications of 30V and 2A. Reducing the value of R3 will increase the maximum output current up to 1A.
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
- P1 = 1K
- R1 = 680R
- R2 = 47K
- R3 = 1R-3W
- Q1 = BC557
- Q2 = BD679 (Darlington)
- D1-D5 = 1N4148
- D6 = 1N4001
More about components
The BD679 is a Darlington transistor, which is a high-gain transistor used to provide a significant amplification of current. This characteristic makes it suitable for driving loads that require substantial current, such as LEDs or small motors. Its specifications – 30V and 2A – indicate its voltage and current handling capabilities. Darlington transistors are often preferred when a large current gain is needed in a compact package.