- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
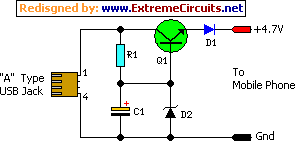
Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
Description
This straightforward circuit delivers a stabilized 4.7 volts, suitable for charging a mobile device. A USB outlet typically provides 5 volts DC at 100mA current, adequate for the gradual recharging of cellular phones. Mobile battery packs are frequently rated at 3.6 volts with capacities ranging from 1000 to 1300 mAh. These battery packs consist of three NiMH or Lithium cells, each with a voltage rating of 1.2 volts. Generally, these battery packs require 4.5 volts at a current of 300-500mA for expedited charging.
However, reduced current charging enhances battery efficiency. The circuit detailed herein furnishes a regulated 4.7 volt output and sufficient current for the slow charging of a mobile phone. Transistor Q1 is implemented to generate the stabilized output. An NPN transistor with moderate power, such as CL100, BD139, or TIP122, can be utilized. A Zener diode D2 controls the output voltage, while D1 safeguards against incorrect polarity in the supply. The initial section of the circuit should be connected to a Type A USB plug.
Connect a red wire to pin 1 and a black wire to pin 4 of the plug for easy polarity identification. Connect the output to a compatible charger socket to establish a connection with the mobile phone. Following the assembly of the circuit, insert the USB plug into the socket and measure the output from the circuit. If the output is satisfactory and the polarity is accurate, then connect it with the mobile phone.
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
- Q1 = BD139
- D1 = 1N4001
- D2 = 4.7V - 1/2W
- R1 = 560R - 1/2W
- C1 = 16V - 100uF
Note:
Incorrect polarity may damage the mobile battery. Therefore, exercise extreme caution.
---More about components
Integrated circuits play a vital role in this circuit. The primary component, Q1, is a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor), a semiconductor device used for amplification and switching. BJTs are characterized by their three terminals: the collector, the base, and the emitter. In this circuit, the BJT acts as a current-controlled current source, allowing a small current flowing into the base to control a larger current flowing between the collector and emitter. The BD139 is a versatile NPN transistor with good switching characteristics and moderate gain, suitable for this application. Its construction enables efficient amplification and switching, crucial for maintaining the regulated output voltage.
---