- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
Description
Utilizing the USB port on a device to charge its batteries is not always practical. What if there is no computer available at the time, or if powering up a computer solely for charging is undesirable? Or perhaps the situation involves travel? Chargers for Mobile Phones, iPods and MP3 players are accessible but often expensive, necessitating separate models for home and car charging.
This charger can be deployed virtually anywhere. Although termed a charger, it fundamentally represents a 5V supply incorporating a USB outlet. The actual charging circuit is integrated within the iPod or MP3 player itself, needing only a 5V supply. Besides charging, this supply can power USB-powered accessories such as reading lights, fans and chargers, specifically for mobile phones.
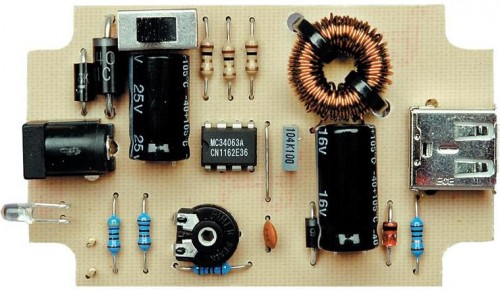
The supply is contained within a small plastic casing featuring a DC input socket at one end and a USB type “A” outlet at the other, for connection to a Mobile Phone, an iPod or MP3 player during charging. An LED indicates when power is accessible at the USB socket. Maximum current output is 660mA, sufficiently high to operate any USB-powered accessory.
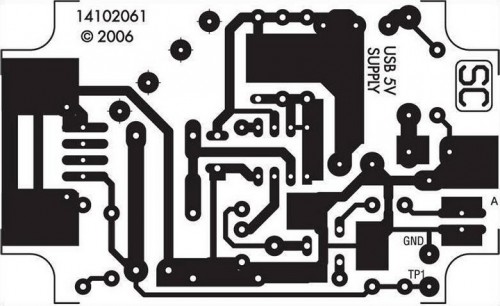
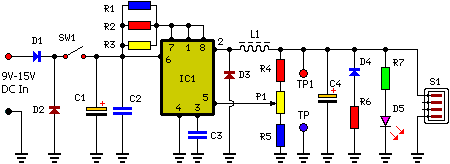
Pictures, PCB and Circuit Diagram:
Parts:
- R1 = 1K
- R2 = 1R-0.5W
- R3 = 1R-0.5W
- R4 = 1K
- R5 = 560R
- R6 = 10R-0.5W
- R7 = 470R
- C1 = 470uF-25V
- C2 = 100nF-63V
- C3 = 470pF
- C4 = 100uF-25V
- D1 = 1N5404
- D2 = 1N4001
- D3 = 1N5819
- D4 = 5.1V-1W Zener Diode
- D5 = 5mm. Red LED
- L1 = 220uH
- S1 = USB 'A' Type Socket
- SW1 = On/Off Switch
- IC1 = MC34063A
Specifications:
- Output voltage ----------------------5V
- Output current ---------------------660mA maximum for 5V out
- Input voltage range ------------------9.5V to 15V DC
- Input current requirement ----------500mA for 9V in, 350mA for >12V input
- Input current with output shorted--- 120mA at 9V in, 80mA at 15V in
- Output ripple ------------------------14mV (from no load to 660mA)
- Load regulation ----------------------25mV (from no load to 660mA)
- Line regulation ----------------------20mV change at full load from 9 to 18V input
- No load input current ----------------20m
(The specification for the computer USB 2.0 port requires the USB port to deliver up to 500mA at an output voltage between 5.25V and 4.375V).
The circuit is based around a MC34063 switch mode regulator. This component offers high efficiency, consequently producing minimal heat inside the enclosure, even when delivering its maximum output current. This circuit is more complex than utilizing a 7805 3-terminal regulator, particularly given the input voltage can reach 15V DC or more. Voltage dissipation in a 7805 regulator could then reach 5W or more at 500mA, which is significantly too high for a 7805, even with a substantial heatsink. Credit for this circuit design goes to SiliconChip, a valued electronics magazine.