- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
Description
Here is the circuit diagram of a cost-effective universal charger for NiCd – NiMH batteries. This circuit is ideal for car applications. It possesses the ability to transform a mains adapter into a charger. It can be used to charge cellular phones, toys, portable devices, video batteries, MP3 players, and more, with selectable charge current. An LED is integrated into the circuit to indicate charging status. It can be constructed on a general-purpose PCB or a veroboard. It is hoped that this circuit will be well-received.
Picture of the circuit:
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
- R1 = 120Ω - 0...5W
- R2 = As Shown in Diagram
- C1 = 220μF - 35V
- D1 = 1N4007
- D2 = 3mm LED
- Q1 = BD135
- J1 = DC Input Socket
Specifications:
- Suitable for in-car use.
- LED charge indication.
- Selectable charge current.
- Charges NiCd or NiMH batteries.
- Transforms a mains adapter into a charger.
- Charges cellular phones, toys, portable devices, video batteries, etc.
Features:
- LED function indication.
- Power supply polarity protected.
- Supply current: Equal to the charge current.
- Supply voltage: From 6.5VDC to 21VDC (depending on the used battery).
- Charge current (±20%): 50mA, 100mA, 200mA, 300mA, 400mA (selectable).
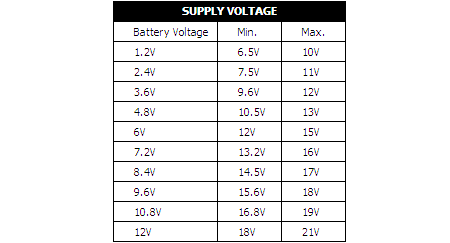
Determining the supply voltage:
The following table indicates the minimum and maximum voltages required to supply the charger. Refer to the supply voltage selection chart below.
Example:
To charge a 6V battery, a minimum supply voltage of 12V is needed, with a maximum voltage of 15V.
Voltage selection:
Determining the charge current:
Before building the circuit, the current required for charging the battery or battery pack must be determined. It is advisable to charge the battery with a current that is 10 times smaller than the battery capacity and to charge it for approximately 15 hours. Doubling the charge current will reduce the charging time by half. The charge current selection chart is located within the diagram.
Example:
A battery pack of 6V / 1000mAh can be charged with 100mA during 15 hours. If faster charging is desired, a charge current of 200mA can be used for approximately 7 hours.
Caution:
Higher charge currents necessitate careful monitoring of the charge time. When using faster charging, it is advisable to fully discharge the battery before charging. Employing a charge current of 1/10 of the capacity will extend the battery’s lifespan. The charge time can easily be doubled without causing damage to the battery.
Note:
Mount the transistor together with the heatsink on the PCB, bending the leads as necessary. Ensure that the metal back of the transistor makes contact with the heatsink. Verify that the leads of the transistor do not touch the heatsink.