- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
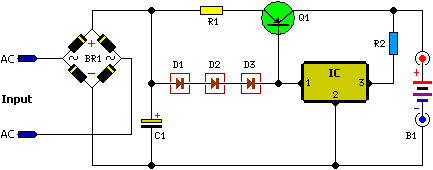
12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
Description
Unlike numerous units, this charging device sustains a continuous charging process at its maximum current flow, only decreasing gradually as the battery approaches full charge. Within this unit, the complete load current provided by the supply transformer/rectifier section reaches 4.4A. This diminishes to 4A at 13.5V, 3A at 14.0V, 2A at 14.5V and 0A at 15.0V.
7815 Regulator
The 7815 is a three-terminal positive voltage regulator integrated circuit. It maintains a steady output voltage of +5V, regardless of variations in the input voltage or the load current. This particular IC is commonly utilized for powering sensitive electronic circuits requiring a stable and precise power supply. It operates over a wide input voltage range and features built-in protection against overcurrent and thermal shutdown, ensuring reliable operation and safeguarding connected components. The 7815 is known for its simplicity, low cost, and wide availability, making it a popular choice in numerous applications. It’s typically encased in a small SOIC-8 package and is easily integrated into circuit designs.
Circuit operation:
Transistor Q1, diodes D1-D3 and resistor R1 constitute a basic current-limiting source. R1 effectively establishes the current passing through Q1 - the voltage across this resistor plus Q1's emitter-base voltage is equivalent to the voltage across D1-D3. Assuming 0.7V across each diode and across Q1's base-emitter junction, the current through R1 is approximately 1.4/0.34 = 4.1A. The IC ensures that Q1 (and thus the current source) remains activated.
When the battery has reached its full charge state, the current through the IC decreases significantly, leading to Q1's deactivation (as there's no longer any base-emitter current flow). R2 limits the current flowing through the regulator, allowing enough current to pass through Q1 to fully activate it for battery voltages up to approximately 13.5V. Reducing the value of R2 effectively raises the final battery voltage by shifting the current cutoff point upwards. Conversely, a diode in series with one of the battery leads will reduce the fully-charged voltage by about 0.7V.
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
- R1 = 0.32R
- R2 = 8.2R
- C1 = 10,000uF - 63V
- D1 = 1N4004
- D2 = 1N4004
- D3 = 1N4004
- Q1 = MJ1504
- IC = 7815 REG
- BR1 = 1N4004x4
- B1 = 12 Volt Battery
Notes:
Charger's input voltages are 20 volt AC R1 and R2 are high wattage resistors, such as 2W, 3W, 5W and above. Select wattage based on your requirements. Q1 and the IC require a suitable heatsink. If mounted on a shared heatsink, the circuit will throttle back if Q1 gets too hot.