- Build a 4.7V USB Mobile Phone Charger Circuit
- Build Your 9V Ni-Cad Battery Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own NiCd Charger: 5V Circuit Design
- Build Your 5V USB Charger Circuit Today!
- Build Your 1.5V Pen Cell Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
- Build a 3.6-6V Cellphone Charger Circuit
- Universal Battery Charger Circuit Diagram – Build Yours!
- Lithium-Polymer Peak Charger: Build Your 600mA Charging Circuit
- SLA Battery Charger Circuit: 2-Step Charging & Safety Features
- Battery Charger Regulator Circuit Diagram – 8V Design
- Build a Safe & Smart 5.6V Charger Circuit
- 12V Car Battery Charger: Build Your Constant Current Circuit
- Micropower Battery Protector Circuit Diagram for 4-10 Cell Batteries
- Build a Stunning Battery Status LED Flasher Circuit
Build Your Own 7.2V Mobile Charger Circuit
Description
Commercial mobile phone chargers are frequently costly. The circuit detailed here offers a cost-effective substitute for charging devices such as Nokia 6110/6150 or other battery packs requiring a voltage of 7.2 volts.
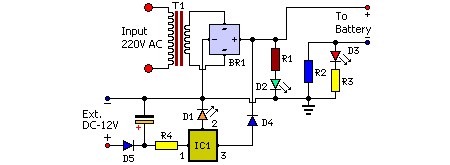
Circuit Diagram:
Parts
- R1 = 1K
- R2 = 47R
- R3 = 10R
- R4 = 47R
- C1 = 1000uF-25V
- D1 = LEDs any color
- D2 = LEDs any color
- D3 = LEDs any color
- D4 = 1N4007
- D5 = 1N4007
- IC1 = LM7806
- T1 = 9VAC Xformer 250mA
- BR1 = Diode bridge 1A
Circuit Operation:
The mains voltage of 220-240V AC is transformed to 9V AC using transformer T1. The transformer’s output is rectified by BR1, and the positive DC supply is directly connected to the charger’s output contact, while the negative terminal is connected through current limiting resistor R2. D2 functions as a power indicator with R1 serving as the current limiter and D3 indicates the charging status. During the charging period, approximately 3 volts drop occurs across R2, which activates D3 through R3.
An alternate DC power source, such as one derived from a vehicle battery, can also power the charger. Following polarity protection by diode D5, resistor R4 limits the input current to a secure value. The 3-terminal voltage regulator LM7806 (IC1) generates a stable DC output of 7.8V, as diode D1 connected between the common terminal (pin 2) and ground rail of IC1 raises the output voltage to 7.8V DC. D1 also operates as a power indicator for the external DC supply. After assembling the circuit on a veroboard, enclose it within a suitable enclosure. A small heat sink is advised for IC1.
LM7806
The LM7806 is a versatile three-terminal positive voltage regulator. This integrated circuit maintains a stable output voltage of 7.8V DC, regardless of variations in the input voltage. It’s commonly used to supply regulated power to sensitive electronic components, providing a consistent voltage supply when the input voltage fluctuates. Its compact size and efficiency make it a popular choice for numerous applications. Its main advantages include a low dropout voltage (typically 2V), meaning it can regulate the output voltage even with a small difference between input and output voltage, and its ability to operate over a wide input voltage range.